Optimization of Brigatinib as New Wild-Type Sparing Inhibitors of EGFR T790M/C797S Mutants.
Li, S., Zhang, T., Zhu, S.J., Lei, C., Lai, M., Peng, L., Tong, L., Pang, Z., Lu, X., Ding, J., Ren, X., Yun, C.H., Xie, H., Ding, K.(2022) ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 196-202
- PubMed: 35178175
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00555
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ER2 - PubMed Abstract:
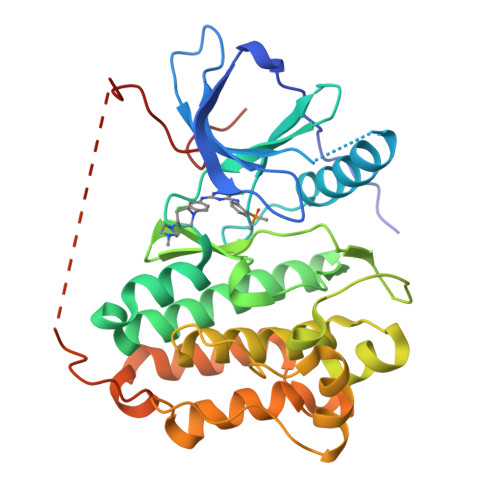
A series of brigatinib derivatives were designed and synthesized as new potent and selective EGFR T790M/C797S inhibitors. One of the most potent and selective compounds 18k strongly suppressed the EGFR L858R/T790M/C797S and EGFR 19Del/T790M/C797S kinases with IC 50 values of 0.7 and 3.6 nM, respectively, which were over 54-fold more potent than the lead compound. 18k also demonstrated promising EGFR T790M/C797S mutant selectivity, and was 94-fold less potent against the wild type EGFR. A cocrystal structure of EGFR T790M/C797S with a close derivative 18f was solved to provide insight on the inhibitor's binding mode. Moreover, compound 18k was orally bioavailable and demonstrated highly desirable PK properties, making it a promising lead compound for further structural optimization.
Organizational Affiliation:
International Cooperative Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization and Innovative Drug Development, Ministry of Education (MOE) of China, Guangzhou City Key Laboratory of Precision Chemical Drug Development, School of Pharmacy, Jinan University, 855 Xingye Avenue East, Guangzhou 511436, China.